Additive Fertigung – 3D Druck in der Massenfertigung
Anders als im Rapid Prototyping geht es in der Additiven Fertigung nicht um die schnelle und kostengünstige Herstellung eines Prototyps oder eines Anschauungsobjektes. Hier wird vielmehr in Masse produziert. Dabei stehen Ihnen für die Additive Fertigung ähnliche Verfahren zur Verfügung – allerdings in anderer Ausführung mit anderen Materialien und vor allem mit gänzlich unterschiedlichen Schwerpunkten in der Herangehensweise.
Von der Reihenfolge her steht die Herstellung eines Prototyps vor der additiven Fertigung. Sind die Probedurchläufe zu Ihrer Zufriedenheit erfolgt und haben Sie Ihren Prototypen so weit perfektioniert, dass Sie in die Massenproduktion einsteigen möchten, ist die Additive Fertigung letztlich die richtige Herangehensweise.

Was genau zeichnet die Additive Fertigung aus?

Als Synonym für diese Art der Fertigung hat sich im Laufe er Jahre der Begriff 3D Druck etabliert. Das hat einen einfachen Hintergrund. Für die verschiedensten Verfahren der Additiven Fertigung wird grundsätzlich eine Form der 3D Fertigung verwendet. Neben diesen beiden Begriffen findet man auch hin und wieder die Formulierung generative Fertigung.
Diese Art der Produktion wird im Bereich der Industrie in den letzten Jahren tatsächlich immer wichtiger. Das liegt beispielsweise daran, dass hier Bauteile mit einem hohen Grad an Individualisierung und Komplexität effektiv hergestellt werden können. Die generative Fertigung ist dabei eine Produktionsart, bei der durch das zufügen von Material ein fertiges Produkt entsteht.

Ausgelegt ist diese Art der Fertigung in erster Linie auf die Massenproduktion. Dabei können Stückzahlen von 1 – 10.000 schnell und problemlos produziert werden. Das Ganze funktioniert ohne den Einsatz von Werkzeugen und auch weitgehend ohne zusätzliche Personalkosten. Allein die Nachbearbeitung der fertigen Produkte kann zusätzliche Personalkosten verursachen. Das ist allerdings abhängig vom gewählten Druckverfahren, den Anforderungen der Kunden an den Dienstleister und natürlich der Komplexität der herzustellenden Objekte.
Worin bestehen die Vorteile der Additiven Fertigung?
Die Vorteile der generativen Fertigung sind durchaus vielfältig.
Generell ist der Materialverbrauch bei dieser Art der Fertigung vergleichsweise gering. Da diese Produktionsart eine Art Schichtdruck ist, wird nur das Material verbraucht, das für den Druck des fertigen Produktes wirklich notwendig ist. Der Verschnitt in Form von möglichen Stützkonstruktionen oder kleinerer Bereiche, die im Rahmen einer Nachbearbeitung abgeschliffen werden müssen, ist sehr gering.
Anders sieht das bei herkömmlichen Produktionsmethoden aus, bei denen beispielsweise aus einem Materialblock ein fertiges Produkt herausgefräst werden muss. Hier ist der Materialverbrauch deutlich höher. In der auf Massenproduktion ausgelegten Fertigung mit dem 3D Druck kommen darüber hinaus Materialien und Techniken zum Einsatz, die das fertige Produkt extrem langlebig und robust werden lassen. So können auf diesem Wege beispielsweise Bauteile für Motoren, die mit Öl, Hitze und Chemikalien in Berührung kommen können, hergestellt werden.

Die fertigen Produkte sind darüber hinaus in der Regel komplett UV-Beständig. Aufgrund der sehr genauen Produktionsmethode können auch Teile für medizinische Zwecke mit 100-prozentiger Genauigkeit auf den jeweiligen Patienten zugeschnitten produziert werden. Generell stellt diese Produktionsmethode eine extrem kostengünstige Variante dar – wenn sie denn richtig eingesetzt wird.
Herkömmliche Herstellungsverfahren steigen oft im Preis, wenn die Produkte komplexer in der Geometrie werden oder wenn mehrere Teile notwendig sind, um Innenräume und andere Besonderheiten in einem fertigen Produkt zu erhalten. Im 3D Druck geht das vollkommen problemlos. Von einem integrierten Gewinde über Hohlräume und Kabelschächte im Produkt selbst bis hin zu komplexen Geometrien und komplizierten Formen.

Dem 3D Drucker ist es letztlich egal, wie das fertige Modell aussieht. Der Druck erfolgt stets einfach nach den Vorgaben der jeweiligen CAD-Datei. Das bedeutet auch, dass der 3D Druck immer lohnender wird, je komplexer und komplizierter die jeweiligen zu fertigenden Teile sind. Bei einfachen Produkten, die ohne große Komplexität daherkommen, lohnt sich hingegen doch eher eine herkömmliche Produktionsart.
Hinzu kommt, dass der 3D Druck inzwischen eine sehr schnelle Produktionsart ist. Zwar hängt auch das natürlich von der jeweils angewandten Technik an. Wir können Ihnen allerdings Produkte innerhalb eines Tages oder aber bei größeren Stückzahlen innerhalb weniger Tage liefern. Die fortlaufende Entwicklung der Additiven Fertigung macht sich auch hier deutlich bemerkbar.

Anders als bei anderen Produktionsverfahren kommt jedes Werkstück aus dem 3D Druck ohne Nähte oder vergleichbare Schwachstellen daher.
Vielmehr ist jedes Produkt der generativen Fertigung ein durchgehendes Stück und somit besonders robust in der Gestaltung.
Die wichtigsten Vorteile auf einen Blick
Die Herstellung im Additiven Fertigungsverfahren erfolgt kosten- und zeiteffizient.
Die Herstellung erfolgt werkzeuglos und mit minimalem Personalaufwand.
Die Umsetzung komplexer und filigraner Geometrien ist problemlos möglich.
Auch innenliegende Strukturen – ob einfach oder komplex – können problemlos umgesetzt werden.
Der Materialverbrauch ist vergleichsweise gering.
Vor der Massenproduktion kann eine Prototypherstellung zur Begleitung der Forschung und Entwicklung erfolgen.
Auf diese Art können sowohl Bauteile als auch Werkzeuge oder komplexe Bestandteile hochwertiger Maschinen, die starken Belastungen standhalten müssen, produziert werden.
Hier können nicht nur Prototypen hergestellt werden, sondern voll funktionsfähige Werkstücke aus allen technischen und industriellen Bereichen.
Die verwendeten Materialien sind extrem langlebig und sehr robust gegen Chemikalien, UV-Einstrahlung und andere belastende äußere Einflüsse.
Verschiedene Verfahren im Bereich der Additiven Fertigung
Es gibt eine ganze Reihe generativer Fertigungsverfahren, die in den unterschiedlichsten Bereichen eingesetzt werden können. Manche eignen sich dabei eher für den privaten Gebrauch oder ausschließlich für den Gebrauch in der Schule oder in der Forschung. Andere wiederum sind auf die Anforderungen im Bereich der Produktion für die Industrie und für komplexe Bereiche wie die Luft- und Raumfahrt zugeschnitten.
Insgesamt zählt man aktuell 11 Verfahren, die in der Additiven Fertigung zum Einsatz kommen. Das Fraunhofer-Institut für Gießerei,- Composite- und Verarbeitungstechnik IGCV und zahlreiche andere vergleichbare Forschungseinrichtungen sind allerdings noch immer dabei, im Bereich der generativen Fertigung zu forschen. Nach eigenen Angaben sind dort aktuell 30 Wissenschaftler mit der fortlaufenden Forschung in Sachen Additive Fertigung beschäftigt.
Die dadurch stetig angestoßene Weiterentwicklung in diesem Bereich nehmen wir als Dienstleister für 3D Druck Produkte natürlich regelmäßig auf und arbeiten sie in unser Leistungsportfolio ein. Unter den zahlreichen Fertigungsmethoden möchten wir an dieser Stelle vor allem zwei erwähnen.
- Das Selektive Lasersintern
- Das Selektive Laserschmelzen
Beide Verfahren sind sich sehr ähnlich – es werden nur gänzlich unterschiedliche Materialien verwendet. Während beim Selektiven Lasersintern Kunststoffpulver zur Anwendung kommt, wird Selektives Laserschmelzen mit Metallpulver gearbeitet.
In beiden Varianten geht es natürlich um Techniken aus dem Bereich des Schichtbaus. Dabei werden in einem geschlossenen Baubereich in einem 3D Drucker Schicht für Schicht aufeinander gefügt. Die jeweiligen Schichten werden mit Laserstrahlen, die auf das genutzte Material angepasst werden, miteinander verschmolzen.
So entstehen gänzlich nahtlose Produkte. Die konkrete Optik des jeweiligen Produktes wird über die vorher zu erstellende CAD-Datei vorgegeben. Diese ist so etwas wie das Bild, das der 3D Drucker „nachzeichnet“.
Diese Materialien kommen hier zum Einsatz
Bei der Materialauswahl können Sie im 3D Druck aus dem vollen schöpfen. Hier kommen sowohl verschiedene Kunststoffe als auch unterschiedliche Metalle zum Einsatz. Welches Material jeweils verwendet wird, richtet sich in erster Linie nach dem Verwendungszweck des fertiggestellten Produktes. Sowohl die Kunststoffpolymere als auch die Metalle werden in Pulverform verarbeitet und anschließend zusammengeschmolzen.
Im Kunststoffbereich gibt es verschiedene Mischpolymere, die beispielsweise mit Glas (PA 12 GF) oder mit Aluminium (Alumide) angereichert sind. Andere wie der Kunststoff PA 12 FR kommt mit einem zusätzlichen Flammschutz daher und kann in besonders gefährlichen Bereichen zum Einsatz kommen.
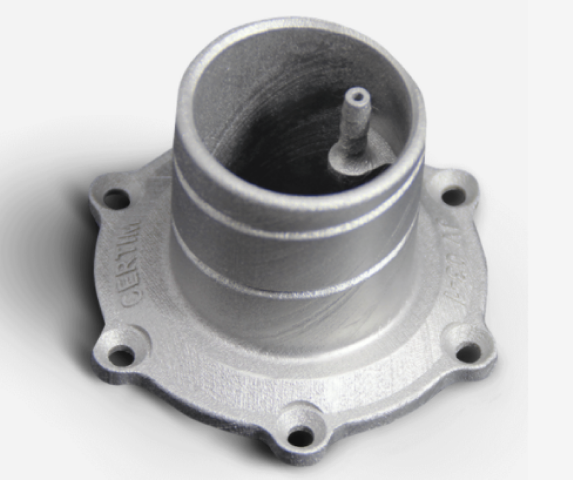


Ähnlich sieht es bei den Metallen aus. Auch hier wird das verwendete Metall nach dem Verwendungszweck des herzustellenden Produktes ausgewählt. Das liegt einfach daran, dass jedes Metall seine eigenen kleinen Vor- und Nachteile mit sich bringt und von der Funktionalität her teilweise eben doch unterschiedlich ist.Unter den Metallen gibt es unter anderem die folgenden:
- Aluminium
- Inconcel
- Edelstahl
- Automobilindustrie
- Werkzeugstahl
- Cobalt-Chrom-Legierung
Diese können als fertiges Produkt sehr hohen Belastungen ausgesetzt sein – sei es in thermischer oder in mechanischer Hinsicht. Daher müssen diese Produkte besonders hochwertig in der Verarbeitung und der Materialauswahl daherkommen. Die Additive Fertigung ist aus diesem Grund hier genau die richtige Wahl.
So funktioniert die Additive Fertigung
Der Ablauf bei der generativen Fertigung sieht in der Regel folgendermaßen aus:
1
Am Anfang steht die Idee für ein neues oder ein verbessertes Produkt
2
In vielen Fällen erfolgt dann als erstes ein Druck im Rapid Prototyping Verfahren, um das geplante Produkt anhand eines Prototyps zu optimieren
3
Nachdem die CAD-Datei nach genauer Studie des Prototyps an den notwendigen Stellen verbessert und angepasst wurde, kann diese neue CAD-Datei nun für die Additive Fertigung genutzt werden.
4
In der Folge geht das von Ihnen geplante Produkt in die Massenproduktion mit Stückzahlen von bis zu 10.000 Stück in einer Produktionsreihe.
Unser Versprechen an Sie in Sachen Additive Fertigung

Die Additive Fertigung ist neben der Rapid-Prototype-Technik eines unserer Haupttätigkeitsfelder. Hier finden Sie eine Menge Know-How, extrem hochwertige Produkte und vor allem die Möglichkeit, bis zur letzten Sekunde Einfluss auf Ihren Entwurf und die daraus resultierenden fertigen Produkte zu nehmen.
Dabei liefern wir Ihnen Produkte aus dem 3D Druck schnell, effizient, kostengünstig und vor allem hochwertig in der Verarbeitung.
Für diese Anwendungsbereiche ist die Additive Fertigung besonders interessant
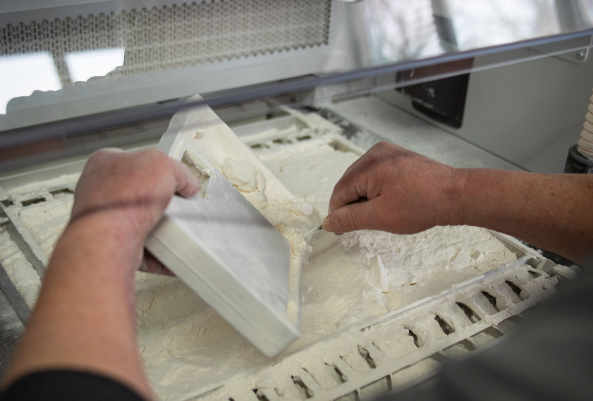

Die generative Fertigung ist in der Auswahl der Anwendungsbereiche kaum ernsthaft eingeschränkt. Das zeigt sich beispielsweise darin, dass in diesem Verfahren gleichermaßen Massen von bis zu 10.000 Stück produziert werden können, wie auch Einzelteile, deren Herstellung in einem anderen Verfahren extrem teuer wäre.
Ob im Modellbau, bei der Produktion von Kleinserien oder auch größerer Produktpaletten – der 3D Druck bietet Ihnen nahezu unendliche Möglichkeiten. Zu den wichtigsten Branchen, in denen diese Produktionsart regelmäßig genutzt wird, gehören unter anderem:
- Medizintechnik
- Luft- und Raumfahrt
- Prothetik
- Automobilindustrie
Zahlreiche Branchen und Unternehmen können von der Anwendung des 3D Drucks profitieren. Ob begleitend in der Entwicklung neuer Produkte oder einfach nur im Zusammenhang mit einer geplanten Produktion verschiedener Bauteile oder anderer Werkstücke. Als erfahrener Dienstleister im Bereich der Additiven Fertigung stehen wir Ihnen in dieser Angelegenheit gern mit Rat zur Seite.

